In this blog, we would like to discuss the Vray CPU vs GPU | Vray for Sketchup Render Engines and how to choose an optimal render engine for your system.
Rendering is one of the most important functions when it comes to processing advanced graphic media, such as VFX and CGI. Simply put, it is the process of generating hyper-realistic or non-realistic images from basic 2D or 3D models.
CPU vs GPU - What's the Difference?
While both types render images, the core difference lies in how they go about handling different sub-tasks involved in the rendering process.
While CPU uses a few dozen of cores to process a render sequentially, GPU utilizes a few thousand cores to perform multiple tasks simultaneously. Knowing the difference could be pivotal in choosing the right renderer for your system.
V-ray offers two rendering engines
GPU (RENDER ENGINE IN V-RAY FOR SKETCHUP)
A Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) is a specialized processor whose job is to rapidly manipulate memory and accelerate the computer for a number of specific tasks that require a high degree of parallelism.
GPU rendering allows V-ray to perform raytracing calculations of your model based on the GPU card installed on your system.
Since GPU’s are specifically designed for massively parallel calculations, they can speed up the rendering process by an order of magnitude. V-ray GPU uses NVidia Cuda or RTX devices to perform its parallel calculations.
V-Ray GPU can be used as a production render or in interactive mode to quickly preview scene changes.
It also supports both the Progressive and Bucket Image Samplers.
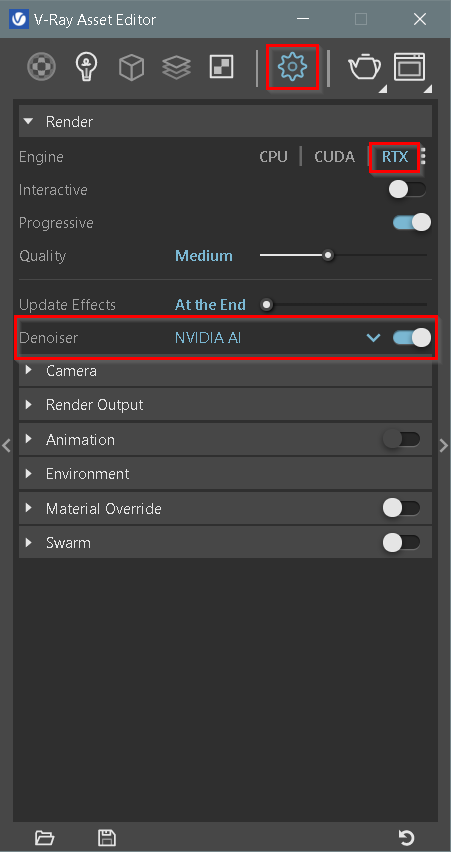
To enable GPU rendering, from V-Ray Asset Editor → Settings tab → Render → select RTX engine and make sure to set your denoiser tab to NVIDIA AI before running a render.
CPU (RENDER ENGINE IN V-RAY FOR SKETCHUP)
A Central Processing Unit (CPU) is the brains of your computer. The main job of the CPU is to carry out a diverse set of instructions through the fetch-decode-execute cycle to manage all parts of your computer and run all kinds of computer programs.
CPU rendering allows V-ray to perform raytracing calculations without installing any graphics card on your system. It simply utilizes your computers CPU efficiently to carry out renders.
A CPU is very fast at processing your data in sequence, as it has few heavyweight cores with high clock speed.
The CPU is latency-optimized and can switch between a number of tasks real quick, which may create an impression of parallelism. Nevertheless, it is fundamentally designed to run one task at a time.
V-Ray CPU can also be used as a production render or in interactive mode to quickly preview scene changes.
It supports both the Progressive and Bucket Image Samplers as well.
Although, CPU rendering is considered the better option to run final renders as they produce higher quality imagery with less noise as compared to V-ray GPU rendering.
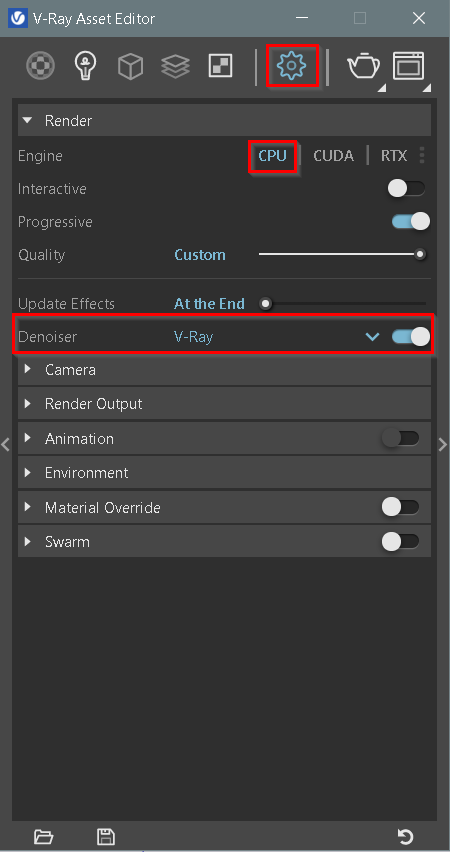
To enable CPU rendering, from V-Ray Asset Editor → Settings tab → Render → select CPU engine and make sure to adjust your denoiser tab to V-ray before running a render.
Advantages of GPU
Advantages of CPU
V-Ray GPU has a number of advantages:
- Graphics cards often outperform CPU devices when it comes to processing parallel tasks, such as raytracing;
- A single machine can host multiple GPU devices but in most cases only a single CPU;
- Hybrid rendering (CUDA only) allows maximum hardware utilization by harnessing the computing power of both GPU and CPU devices;
- V-Ray GPU has all the required features to be production ready;
V-Ray CPU advantages:
- Allows rendering complex scenes requiring a substantial amount of memory;
- Supports all V-Ray features;
- Does not pre-occupy single-GPU machines during rendering
CUDA (Compute Unified Device Architecture)
Although we have covered the two main V-ray rendering engines. There is a third rendering engine known as CUDA.
This method of rendering is widely termed as ‘Hybrid Rendering’ as it employs both CPU and GPU to conduct its raytracing calculations.
The hybrid rendering mode does not require any special drivers. Furthermore, you can use the CPU as a CUDA device even if you don’t have an NVIDIA GPU and/or NVIDIA drivers installed. Meaning, this mode can be used on computers that don’t even have GPUs.
The hybrid render engine running on a CPU supports the same features as the regular V-Ray GPU CUDA engine.
CUDA can also be used as a production render or in interactive mode to quickly preview scene changes. It also supports both the Progressive and Bucket Image Samplers.
To enable CUDA rendering, from V-Ray Asset Editor → Settings tab → Render → select CUDA engine and make sure to set your denoiser tab to NVIDIA AI before running a render.

If you would like to learn how to create photorealistic renders, do check out our premium Sketchup & Vray Course for Interior Design