The Role of Photorealism in Modern Architecture

Photorealism has become a pivotal aspect of modern architecture, shaping the way architects conceptualize and present their designs. In today’s digital age, where visual representation plays a crucial role in communication and decision-making, photorealistic rendering techniques have emerged as powerful tools for architects to convey their ideas with unparalleled realism and precision. This blog explores the significance of photorealism in modern architecture and its impact on the design process, client communication, and architectural visualization.
Evolution of Architectural Visualization
Traditional Methods
- Hand-drawn Sketches and Blueprints: Traditional architectural visualization relied on hand-drawn sketches, blueprints, and physical models to convey design concepts to clients.
- Introduction of CAD Software: The advent of computer-aided design (CAD) software revolutionized architectural visualization, allowing architects to create digital models of their designs with greater precision and efficiency.
Emergence of Photorealistic Rendering
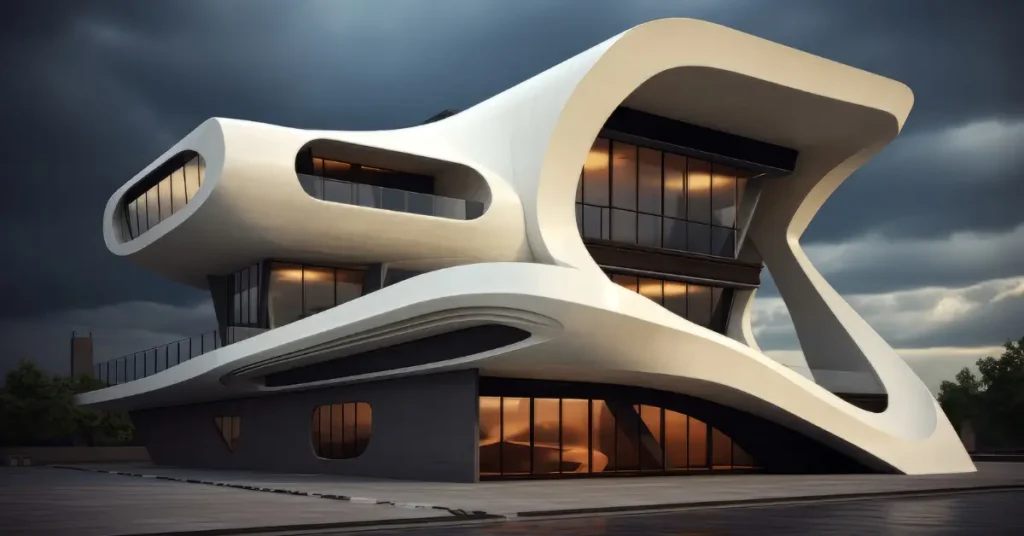
- Advancements in Technology: The evolution of rendering techniques has enabled architects to create lifelike representations of their designs, offering clients and stakeholders a realistic preview of the final built environment.
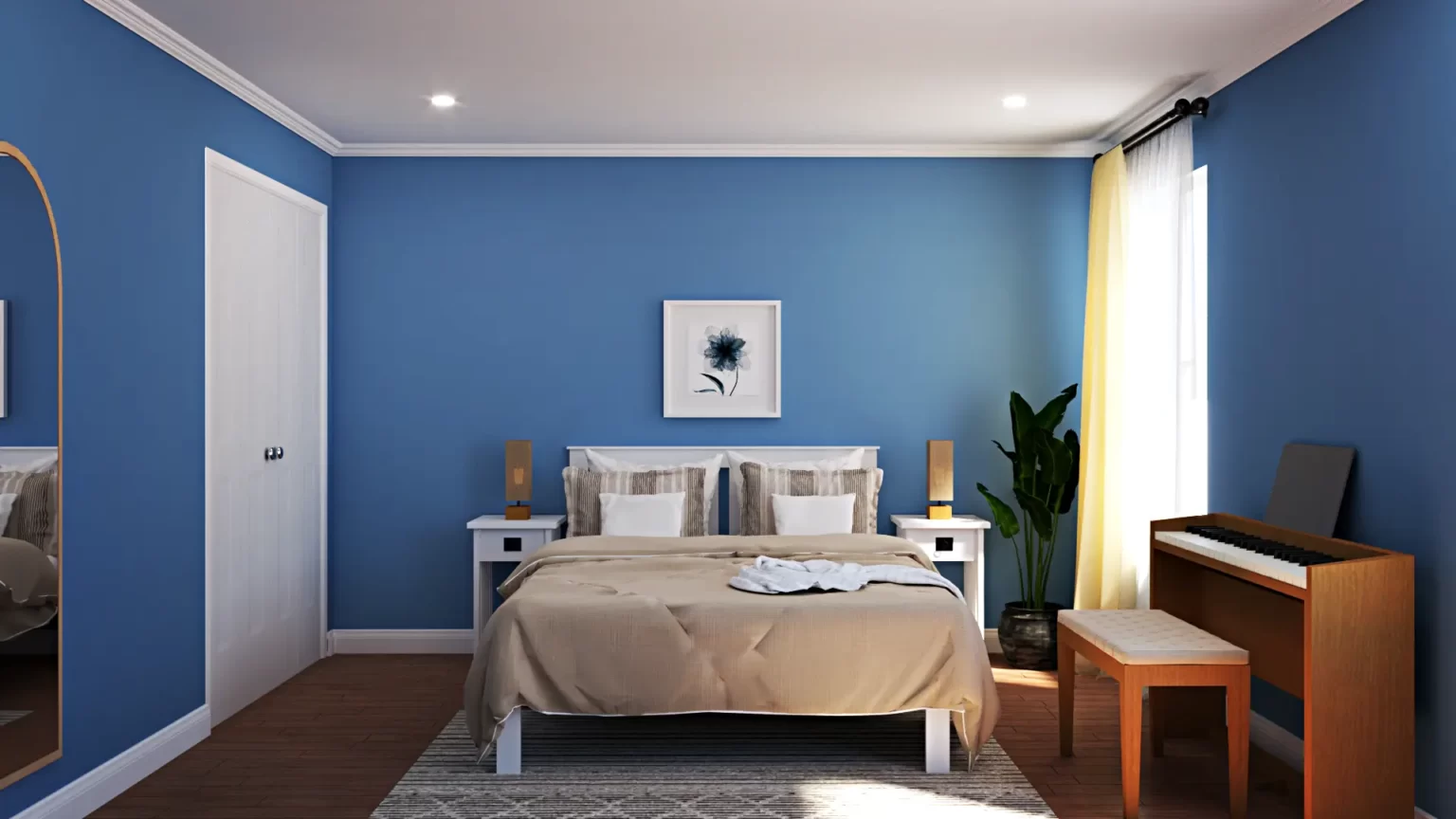
- Realism and Detail: Photorealistic rendering provides a clear and detailed representation of the proposed architectural design, enabling better understanding and visualization of spatial relationships, materials, and finishes.
Advantages of Photorealistic Rendering
Enhanced Design Communication
- Clarity and Detail: Photorealistic renderings offer clients and stakeholders a realistic preview of the final built environment, facilitating better understanding and visualization of design concepts.
- Better-informed Decision-making: By presenting highly detailed and realistic images of architectural spaces, materials, and lighting conditions, architects can effectively communicate design concepts and facilitate better-informed decision-making.
Iterative Design Process
- Exploration of Design Options: Photorealistic rendering allows architects to explore various design options and iterations rapidly, leading to better-informed design decisions and optimized outcomes.
- Efficiency and Optimization: By generating realistic visualizations of different architectural configurations, materials, and finishes, architects can evaluate the aesthetic and functional implications of each design decision more efficiently.
Techniques and Technologies
Ray Tracing and Global Illumination
- Simulation of Light Rays: Ray tracing algorithms simulate the behavior of light rays in a virtual environment, allowing for accurate light interactions and reflections.
- Enhanced Realism: Global illumination techniques further enhance realism by considering indirect lighting effects, resulting in lifelike renderings with realistic lighting conditions.
Texture Mapping and Material Simulation
- Application of Textures and Materials: Texture mapping techniques enable architects to apply realistic textures and materials to digital surfaces, enhancing the visual fidelity of architectural renderings.
- Simulation of Physical Properties: Material simulation algorithms simulate the physical properties of materials, such as reflections, refractions, and surface roughness, contributing to the overall realism of the rendering.
Challenges and Considerations
Computational Resources
- Hardware Requirements: Generating high-quality photorealistic renderings often requires significant computational resources, including powerful hardware and rendering software.
- Time and Resource Constraints: Architects must consider the time and resources required to produce renderings, particularly for large-scale projects with complex designs.
Artistic Interpretation
- Balance Between Realism and Creativity: While it is essential to accurately represent architectural details and materials, architects must also leverage rendering techniques to evoke emotion and narrative in their visualizations.
- Client Expectations: Managing client expectations is crucial when presenting photorealistic renderings, as they may raise unrealistic expectations regarding the final built environment.
Future Trends and Innovations
Real-time Rendering Engines
- Interactive Visualization: Real-time rendering engines enable architects to visualize designs interactively, facilitating immediate feedback and iteration during the design process.
- Improved Efficiency: These engines leverage the power of GPU acceleration to achieve high frame rates and responsiveness, revolutionizing the way architects create and explore architectural visualizations.
Virtual Reality (VR) Experiences
- Immersive Visualization: VR technology offers immersive and interactive experiences that allow users to explore architectural designs in a virtual environment.
- Enhanced Engagement: Architects can create VR walkthroughs and experiences that provide clients and stakeholders with a compelling preview of the proposed built environment, fostering greater engagement and understanding.
Conclusion
Photorealistic rendering plays a vital role in modern architecture, offering architects a powerful tool for visualizing, communicating, and presenting their designs. From enhancing design communication to facilitating decision-making and marketing, photorealism has become an indispensable aspect of the architectural process. As rendering technologies continue to evolve and innovate, architects will undoubtedly leverage photorealism to push the boundaries of architectural visualization and create compelling designs that shape the built environment for generations to come.